News
New Clues to the Genetics Roots of Autism
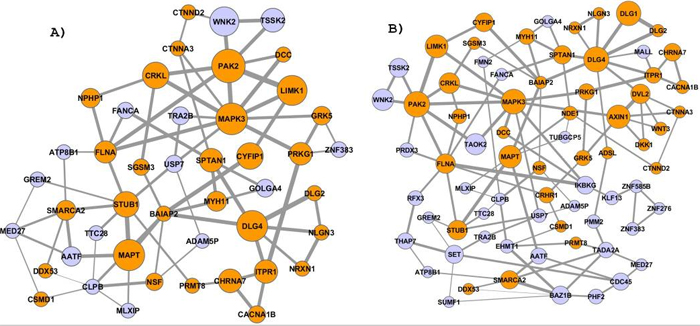
Gene clusters found using NETBAG analysis of de novo CNV regions observed in autistic individuals. A) The highest scoring cluster obtained using the search procedure with up to one gene per each CNV region. B) The cluster obtained using the search with up to two genes per region.
Identification of complex molecular networks underlying common human phenotypes is a major challenge of modern genetics. A new network-based method developed at the lab of Dennis Vitkup was used to identify a large biological network of genes affected by rare de novo copy number variations (CNVs) in autism. The genes forming the network are primarily related to synapse development, axon targeting, and neuron motility. The identified network is strongly related to genes previously implicated in autism and intellectual disability phenotypes.
These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that significantly stronger functional perturbations are required to trigger the autistic phenotype in females compared to males. Overall, the analysis of de novo variants supports the hypothesis that perturbed synaptogenesis is at the heart of autism.